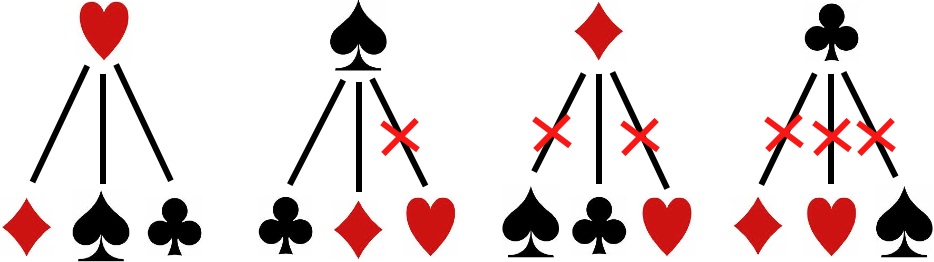
思路简述:
一个全排列其实就是一条把数组无重复遍历一遍的DFS过程
思路一:简单回溯,
- 一个List存遍历路径,从第N个“结点”到第N+1个“结点”是只需要找一个未遍历的结点就行
- 一个关键点在于查找 下一个可遍历“结点”, 可以用SET辅助List存放已遍历结点,List中存遍历书序(文中方法未用SET,复杂度较高,但是可以在Leetcode上AC);也可用一个数据结构完成: LinkedHashMap,即可保存插入顺序,也可O(1)判断是否存在某元素。
- 回溯: 选中某一子“结点”递归下去之后,要回溯查找另一“子节点”,这就是回溯的过程,通过把某时刻路径中最后结点删除,添加下一“子节点”实现
代码
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] num) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
if(num == null || num.length < 1) return res;
bt(res, new ArrayList<Integer>(), 0, num);
return res;
}
public void bt(List<List<Integer>> res, final List<Integer> cur, int now, int[] num){
int length = num.length;
if(cur.size() >= length) {
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(){
{
addAll(cur);
}
});
return ;
}
for(int i = now; i < length || i % length < now; i++){//回溯
if(cur.contains(num[i % length])) continue;//判断回溯的元素是否已加入当前组合中
cur.add(num[i % length]);
bt(res, cur, (i + 1)% length, num);
cur.remove(cur.size() - 1);
}
}
思路二:
基于思路一,不需要辅助List存放遍历路径,原数组就是遍历路径
每次寻找下一遍历结点的过程可以转化为,将后一结点交换到当前结点的过程
还原交换的过程就是回溯的过程
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] num) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
if(num == null || num.length < 1) return res;
bt(res, new ArrayList<Integer>(), 0, num);
return res;
}
public void bt(List<List<Integer>> res, final List<Integer> cur, int now, final int[] num){
int length = num.length;
if(now >= length) {
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(){
{
for(int i: num)
add(i);
}
});
return ;
}
for(int i = now; i < length; i++){
swap(num, now, i);
bt(res, cur, now + 1, num);
swap(num, now, i);
}
}
public void swap(int[] nums, int idx1, int idx2){
int temp = nums[idx1];
nums[idx1] = nums[idx2];
nums[idx2] = temp;
}